Ore formation/ Ore genises terms
Exsolution
In mineralogy, process through which an initially homogeneous solid solution separates into at least two different crystalline minerals without the addition or removal of any materials. In most cases, it occurs upon cooling below the temperature of mutual solubility or stability of the solution. The sodium-rich feldspar albite (NaAlSi3O8) and the potassium-rich feldspar orthoclase (KAlSi3O8), for example, may exist in a homogeneous solid solution above 650° C (1,200° F), but below that temperature exsolution will occur.
Orogeny,
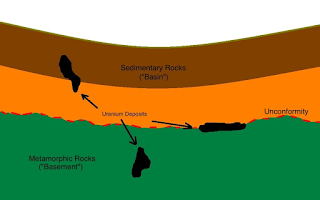
Orogeny, mountain-building event, generally one that occurs in geosynclinal areas. In contrast to epeirogeny, an orogeny tends to occur during a relatively short time in linear belts and results in intensive deformation. Orogeny is usually accompanied by folding and faulting of strata, development of angular unconformities (interruptions in the normal deposition of sedimentary rock), and the deposition of clastic wedges of sediments in areas adjacent to the orogenic belt. Regional metamorphism and magmatic activity are often associated with an orogenic event as well. Orogenies may result from subduction, terrane accretion (landmass expansion due to its collision with other landmasses), the underthrusting of continents by oceanic plates, continental collisions, the overriding of oceanic ridges by continents, and other causes. See plate tectonics.
Accretion
Accretion, in geology, is a process by which material is added to a tectonic plate or a landmass. This material may be sediment, volcanic arcs, seamounts, or other igneous features. |
| Oceanic-continental convergence: The required conditions for plate accretion |
Accretion involves the addition of material to a tectonic plate. When two tectonic plates collide, one of the plates may slide under the other, a process known as subduction. The plate which is being subducted, is floating on the asthenosphere and is pushed against the other, over-riding plate. Sediment on the ocean floor will often be scraped from the subducting plate. This causes the sediment to accumulate as a mass of material called an accretionary wedge (accretionary prism), which attaches itself to the upper plate. Volcanic island arcs or seamounts may collide with the continent, and as they are of relatively light material (i.e. low density) they will often not be subducted, but are added to the side of the continent.







Comments
Post a Comment