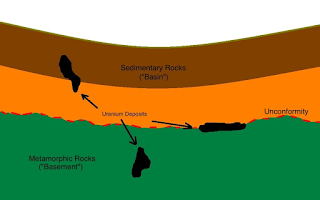
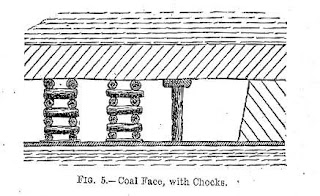
The Common Rock Forming Minerals

The most Common rock forming minerasl are listed below. 1- Silicates The felspars These are complex silicates of aluminium with potash, soda or lime and are most abundant in igneous rocks. Potash felspar, also known as orthoclase, is the most common type. It is white, grey or pink in colour with a glassy lustre. When weathered it leaves a hydrated silicate of aluminium known as kaolin or china clay. the soda and lime felspars are known as plagioclase. they also decompose and disintegrate in a similar way. [lagioclase felspars occur in most igneous rocks, especially the darker varieties rich in lime. the specific gravity of felspars is between 2.6 - 2.7 and its hardness on the scale of Mohs is 6. Mica this occurs as a white variety known as muscovite (a silicate of aluminium and potassium) and as a black variety known as black mica or biotite (a silicate of aluminium, iron and magnesium). the mica can be easily scratched by fingernail and has a well-developed cleavage. it is a common co...