strata-bound deposits
strata-bound deposits
Strata-bound deposit types, minerals.
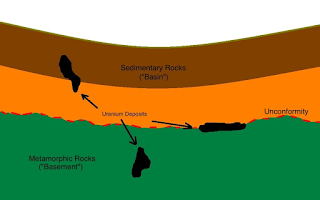
Strata-bound deposits are mineral deposits that are confined to specific layers or strata of rock. There are several types of strata-bound deposits, including:
Sedimentary exhalative (SedEx) deposits: These form from hot fluids that exsolve from volcanic or hydrothermal systems and deposit minerals in layers of sedimentary rock. Examples include sedimentary copper and lead-zinc deposits.
Skarn deposits: These form from the alteration of limestone or dolostone by hot fluids, resulting in the precipitation of iron, lead, zinc, and other metals in the altered rock. Examples include the iron-copper skarns of the American Cordillera and the lead-zinc-silver skarns of the Mediterranean region.
Volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposits: These form from the precipitation of sulfide minerals in submarine volcanic environments. Examples include the massive sulfide deposits of the Iberian Pyrite Belt and the Noranda deposits in Canada.
Stratiform copper deposits: These are copper deposits that are stratiform in shape and occur in sedimentary rocks. Examples include the copper deposits of the Central African Copperbelt and the Kupferschiefer of Poland.
Minerals commonly found in strata-bound deposits include sulfides (such as pyrite, sphalerite, and chalcopyrite), oxides (such as hematite and magnetite), carbonates (such as siderite and calcite), and silicates (such as garnet and epidote).







Comments
Post a Comment