Timber support in coal mine
Side Support:
Wooden laggings are placed tight between vertical props and pillar where the sides are weak and need support. Sometimes the timber set of prop and bar has to resist pressure from sides which tend to crush into the roadways. Notching is useful in such cases. The props should be set at an angle of 14° to 20° off the vertical and the feet well sunk into the floor.
An alternative method of resisting side pressure is to sink the props well into the floor and to reinforce the timber-set by an additional bar or stretcher (dotted bar in fig), which may be nailed to the props. As this reduces effective height of roadway, its use may not be advisable in roadways of less than 2 m height, used by basket loaders.
 |
| Reinforced Timber set or chockmate |
 |
| Notched Prop |
Support of a Roadway:
Where the roof of a roadway is bad over some distance bars resting in holes of coal pillars and tightened against the roof by wooden laggings may be erected at intervals of 2 to 3 m. If the coal pillars are not strong enough or the road is through a fault zone, the wooden bars are supported on timber props.
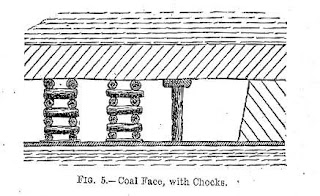
This is a common practice. Where the roof pressure is likely to be heavy bars may be supported on timber chocks. Below figure shows a methos supporting a wide jundtion by coas and bars. No props should be erected at such a place where they are likely to be dislodged by moving or derailed and runaway tubs. The bars may sometimes be placed on bricks walls constructed on solid foundation of coal floor with 150 mm layer of concrete at the base.
 |
| Support of junction by cogs and bars |
 |
| Support of junction by props and bars |
Clearing Up Heavy Roof Fall:
Such occasions arise sometimes in mines. As a result of roof fall the haulage rope and cables may be buried and if the debris blocks up the roadway right upto the roof, ventilation is affected if there is no other path for ventilating air.
If the roadway is the only access to in bye workings men at the workings are stranded. It is therefore, necessary to clear up the roof fall speedily and only experienced timber men should be entrusted with the job. Power from the buried cable should be switched off.
In all such cases where the roof fall has to be cleared up work must always be done from a safe place and as the debris is cleared, supports should be set so that the place out-bye is always free from danger. In Fig. 9.12 sets of props and ban are erected at a, b, c after dressing loose roof rock and the approaches to the fall made safe. Cogs are erected at the junction as shown at d, and bars placed over the cogs. Standing at the safe place near the cogs, the loose or hanging pieces in the roof are dressed down by the timber men with a button. The debris of roof fall is then removed by workers and packed up in the nearby galleries but where speed is essential, it may be packed along the sides of the haulage road itself.
Temporary props with thick and wide sole plate and top lids are erected on the debris to support the roof temporarily for safety of debris-clearing majdoors. The roadway is thus partially cleared so as to establish ventilation and to remove the trapped men. If the haulage rope is also freed by clearing the debris it is used for expediting the operation by loading debris in tubs.
The temporary supports are then replaced by permanent ones like cogs and bars for at least 15 m on all sides of the junction. If the place is important and life of the roadway justifies the expenditure, the place may be supported by brick-wall over which girders and corrugated galvanised iron (C.G.I.) sheets are placed. The cavity between the C.G.I, sheets and the roof is packed with boiler ash, or cogs may be erected over the C.G.I, sheets to support the roof above. This permanent measure, however, takes quite some time.
 |
| Clearing up heavy roof fall |
Systematic Timbering:
“Systematic timbering” is the term used for erecting supports in such a manner that the distances between supports are according to a specified pattern as laid down by the Manager and approved by the Directorate of Mines Safety.
Systematic timbering is essential in the district of bord and pillar workings where splitting of pillars or depillaring is going on, on every long wall working face, in every working in a disturbed or crushed ground (e.g. fault zone) and etc.
The type of supports to be erected, whether cogs, props, or bars arc also specified in the order governing systematic timbering. In every case of systematic timbering, it is essential that additional supports shall be erected as and when necessary. Manager has to hand over copies of systematic timbering rules to all the supervising officials and has to post such copies at conspicuous place in the mine.
Withdrawal of Supports:
When props, bars or cogs have to be withdrawn it is prohibited by law to withdraw them by hammering. Suitable safety prop-withdrawer like the Sylvester prop-withdrawer has to be used.
It is an advantage to fix the chain C on the prop P G in such a manner before withdrawal that when the chain is pulled and is getting tightened, the prop receives a slight twist – on action which loosens the prop in its position.
In the depillaring areas, a long chain is often required in place of the chain C. To avoid such long length, a flexible wire rope with steel core (e.g. 15 mm dia. Coal-cutting machine haulage rope) having capels at both the ends may be used in conjunction with the usual 6 m long chain.
Where the roof is high, a suitable anchor prop may not always be available for operation of prop withdrawer. In such case a piece of rail is fixed in a half metre deep hole in the floor. It serves the purpose of anchor prop.
Alternatively, a strong bar fixed in the coal pillar may be used to serve the object. Care should be taken to see that the anchor prop or other props which provide safety to the timber men operating the prop withdrawer should not be dislodged by the prop under withdrawal when it is released
 |
| Sylvester prop withdrawer |












Comments
Post a Comment